This post contains affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases
Understanding cholesterol levels is crucial for maintaining a healthy heart. Cholesterol is a type of fat found in the bloodstream that plays a vital role in various bodily functions, including the production of hormones and the digestion of fats.
Managing cholesterol levels effectively is key to preventing heart disease. High levels of bad cholesterol can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
By learning about the importance of cholesterol levels and how to manage them, individuals can take proactive steps towards a healthier lifestyle.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding cholesterol’s role in the body is vital for heart health.
- Managing cholesterol levels can prevent heart disease.
- High bad cholesterol levels can lead to plaque buildup in arteries.
- Proactive management of cholesterol levels contributes to a healthier lifestyle.
- Knowledge about cholesterol is key to making informed health decisions.
Understanding Cholesterol: The Basics
Despite its negative connotation, cholesterol is essential for numerous bodily functions, including the production of cell membranes and hormones. Maintaining healthy cholesterol levels is crucial for overall health.
What is Cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a fatty substance found in the bloodstream. It is produced by the liver and is also obtained from certain foods. Cholesterol is vital for producing hormones, vitamin D, and substances that help digest foods.
Types of Cholesterol: HDL vs. LDL
There are two main types of cholesterol: HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) and LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein). HDL is often referred to as “good” cholesterol because it helps remove other forms of cholesterol from the bloodstream. LDL, on the other hand, is considered “bad” cholesterol as high levels can lead to plaque buildup in arteries.
| Type of Cholesterol | Function | Impact on Health |
|---|---|---|
| HDL (Good Cholesterol) | Removes excess cholesterol from the bloodstream | High levels are associated with lower risk of heart disease |
| LDL (Bad Cholesterol) | Transports cholesterol to various tissues | High levels can lead to plaque buildup and increased risk of heart disease |
The Role of Cholesterol in the Body
Cholesterol plays a critical role in the body, including the production of cell membranes, hormones such as estrogen and testosterone, and vitamin D. It is also essential for the production of bile acids, which help digest fats.
Maintaining a balance of cholesterol is key. While it is essential for various bodily functions, excessive levels, particularly of LDL cholesterol, can lead to health issues such as atherosclerosis and heart disease.
The Importance of Cholesterol Levels
Monitoring cholesterol levels is crucial for maintaining heart health and preventing cardiovascular diseases. High or unbalanced cholesterol levels can lead to serious health issues, including heart attacks and strokes. By understanding cholesterol ratios, individuals can better manage their heart health.
Why Monitoring Cholesterol is Essential
Regular monitoring of cholesterol levels is vital because it helps in early detection of potential heart problems. Understanding cholesterol ratios is key to assessing the risk of heart disease. This involves measuring the levels of different types of cholesterol, such as HDL (good cholesterol) and LDL (bad cholesterol).
By keeping track of these levels, individuals can make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and other lifestyle factors that impact cholesterol. For instance, a high LDL level may necessitate dietary changes or increased physical activity.
How Cholesterol Affects Heart Health
Cholesterol affects heart health by influencing the formation of plaque in the arteries. When LDL cholesterol levels are high, it can lead to plaque buildup, narrowing the arteries and increasing the risk of heart disease. Conversely, HDL cholesterol helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream, reducing the risk of heart disease.
Maintaining a healthy balance between HDL and LDL cholesterol is crucial. Understanding cholesterol ratios helps in assessing this balance. A higher ratio of HDL to LDL is generally considered better for heart health.
| Cholesterol Type | Desirable Level | Borderline Level | High Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDL Cholesterol | <100 mg/dL | 100-129 mg/dL | ≥130 mg/dL |
| HDL Cholesterol | ≥60 mg/dL | 40-59 mg/dL | <40 mg/dL |
| Total Cholesterol | <200 mg/dL | 200-239 mg/dL | ≥240 mg/dL |
By monitoring and managing cholesterol levels effectively, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of heart disease. Regular check-ups and a healthy lifestyle are key components of maintaining optimal cholesterol levels.
Factors Influencing Cholesterol Levels
The implications of high cholesterol are significant, and understanding the factors that contribute to it is essential. Cholesterol levels are influenced by a combination of lifestyle choices and genetic predispositions.
Diet and Nutrition
Diet plays a crucial role in determining cholesterol levels. Consuming foods high in saturated fats and cholesterol can increase levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol. On the other hand, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help improve levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) or “good” cholesterol.
Nutritional Tips:
- Choose healthy fats like avocado and nuts.
- Limit intake of saturated and trans fats.
- Increase consumption of soluble fiber found in oats, barley, and fruits.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is another significant factor that can influence cholesterol levels. Exercise can help raise HDL cholesterol and lower LDL cholesterol. The American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
“Regular exercise not only improves cholesterol levels but also contributes to overall cardiovascular health.” – American Heart Association
Genetics and Family History
Genetics and family history also play a critical role in determining cholesterol levels. Individuals with a family history of high cholesterol are more likely to develop high cholesterol themselves. Genetic conditions such as familial hypercholesterolemia can significantly impact cholesterol levels.
Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed decisions about their lifestyle and dietary choices to manage their cholesterol levels effectively.
How to Test Cholesterol Levels
Monitoring cholesterol levels is a vital part of a healthy lifestyle. It helps in understanding the risk of heart diseases and taking preventive measures. Testing cholesterol levels is a straightforward process that involves a simple blood test.
Understanding Lipid Panels
A lipid panel is a comprehensive test that measures various components of your cholesterol, including HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein), LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein), and triglycerides. HDL is often referred to as “good” cholesterol because it helps remove other forms of cholesterol from your bloodstream. On the other hand, LDL, or “bad” cholesterol, can lead to plaque buildup in your arteries.
The lipid panel provides a detailed picture of your cholesterol levels, helping healthcare providers assess your risk of heart disease and develop a plan to manage your cholesterol.
When to Get Tested
The frequency of cholesterol testing depends on several factors, including your age, risk factors for heart disease, and your current health status. Generally, adults aged 20 and older should have their cholesterol levels checked every 4 to 6 years. However, if you have risk factors such as a family history of high cholesterol or heart disease, your doctor may recommend more frequent testing.
It’s also important to get tested if you’re starting or changing treatments for high cholesterol. Regular monitoring can help determine the effectiveness of your treatment plan and whether any adjustments are needed.
Understanding your test results is crucial. Your healthcare provider can explain what your numbers mean and provide guidance on how to improve your cholesterol levels if necessary.
Ideal Cholesterol Levels Explained
Ideal cholesterol levels play a vital role in preventing heart disease. Understanding what constitutes normal, high, borderline, and low cholesterol levels is essential for assessing cardiovascular risk.
What are Normal Levels?
Normal cholesterol levels vary based on factors such as age, gender, and overall health. Generally, a total cholesterol level of less than 200 mg/dL is considered desirable. LDL (bad) cholesterol should be below 100 mg/dL, while HDL (good) cholesterol should be 60 mg/dL or higher.
Risk Levels: High, Borderline, and Low
Cholesterol levels are categorized into different risk levels. A total cholesterol level between 200-239 mg/dL is considered borderline high, while 240 mg/dL or higher is considered high. For LDL cholesterol, levels between 130-159 mg/dL are borderline high, and 160 mg/dL or higher is considered high. Conversely, very low LDL levels (below 40 mg/dL) can also pose health risks.
Understanding these categories helps individuals assess their risk and make informed decisions about their lifestyle and treatment options. Regular monitoring and consultation with healthcare professionals are crucial for managing cholesterol levels effectively.
- Total Cholesterol: Less than 200 mg/dL is desirable.
- LDL Cholesterol: Below 100 mg/dL is optimal.
- HDL Cholesterol: 60 mg/dL or higher is considered good.
By maintaining ideal cholesterol levels, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of heart disease and promote overall well-being.
The Consequences of Uncontrolled Cholesterol
Maintaining healthy cholesterol levels is vital, as deviations in either direction can have significant health consequences. Cholesterol is a critical component of our bodily functions, but when its levels become imbalanced, it can lead to serious health issues.
Uncontrolled cholesterol, whether too high or too low, poses significant risks to our health. High cholesterol is often associated with an increased risk of heart disease, while low cholesterol can have its own set of health implications. Understanding these risks is crucial for effective management and prevention.
Health Risks Associated with High Cholesterol
High cholesterol is a well-known risk factor for heart disease. When cholesterol levels are elevated, it can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, known as atherosclerosis. This condition can cause the arteries to narrow and harden, restricting blood flow and potentially leading to heart attacks or strokes.
“High cholesterol is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, which is the leading cause of death globally.”
The risks associated with high cholesterol are not limited to cardiovascular disease. It can also impact other aspects of health, such as increasing the risk of peripheral artery disease.
| Condition | Risk Associated with High Cholesterol |
|---|---|
| Heart Disease | Increased risk of heart attacks and strokes |
| Peripheral Artery Disease | Narrowing of arteries in the legs and arms |
How Low Levels Can Also Be Problematic
While high cholesterol is a more commonly discussed risk, low cholesterol levels can also have health implications. Research has suggested that very low cholesterol levels may be associated with an increased risk of certain health conditions, such as depression and anxiety.
Additionally, low cholesterol can be a marker of underlying health issues, such as malabsorption or hyperthyroidism. It is essential to identify the cause of low cholesterol to address any potential health concerns.
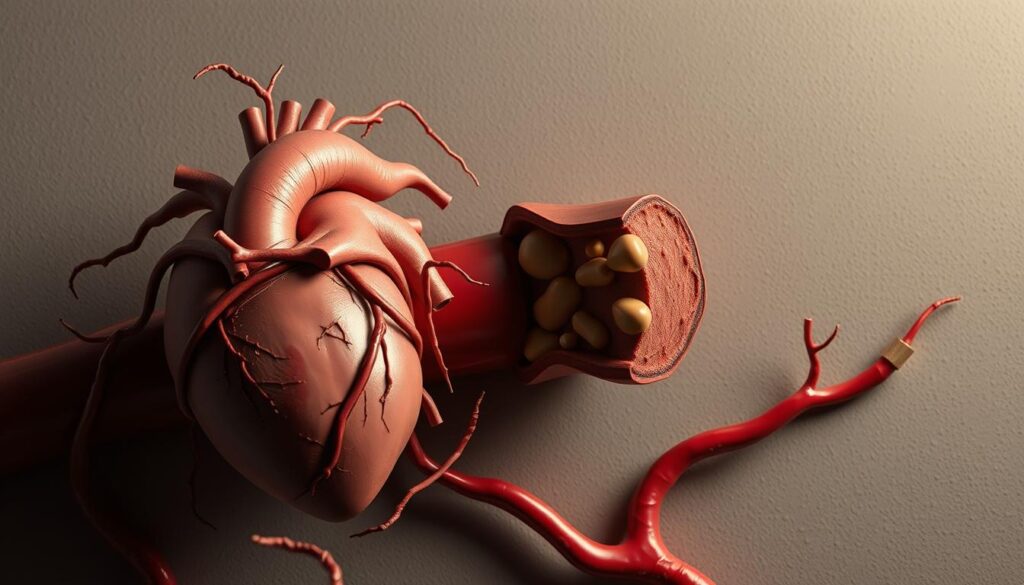
In conclusion, maintaining cholesterol levels within a healthy range is crucial for overall health. Both high and low cholesterol levels can have significant health consequences, emphasizing the need for awareness, monitoring, and management.
Dietary Choices for Healthy Cholesterol
The food we eat has a profound effect on our cholesterol levels, making informed dietary choices essential. A diet rich in certain nutrients can help improve HDL (good) cholesterol, while avoiding specific foods can lower LDL (bad) cholesterol.
Foods That Improve HDL Cholesterol
Increasing HDL cholesterol is beneficial for overall heart health. Certain foods have been shown to boost HDL levels:
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which are known to increase HDL cholesterol.
- Olive Oil: Rich in monounsaturated fats, olive oil can help raise HDL levels.
- Avocados: Avocados are a good source of monounsaturated fats and can contribute to higher HDL cholesterol.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and chia seeds are examples of nuts and seeds that can help improve HDL levels.
Foods to Avoid for Lowering LDL Cholesterol
Reducing LDL cholesterol is crucial for minimizing the risk of heart disease. Limiting or avoiding certain foods can help achieve this:
- Trans Fats: Found in processed and fried foods, trans fats can significantly raise LDL cholesterol.
- Saturated Fats: Limiting saturated fats, commonly found in red meat and full-fat dairy products, can help lower LDL cholesterol.
- High-Cholesterol Foods: Foods high in cholesterol, such as egg yolks and organ meats, should be consumed in moderation.
By incorporating HDL-boosting foods and limiting LDL-raising foods, individuals can make significant strides in managing their cholesterol levels through dietary choices alone.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Cholesterol
To manage cholesterol levels, it’s essential to incorporate healthy lifestyle habits. Lifestyle changes can significantly impact your overall cholesterol levels and heart health. By focusing on regular physical activity and effective stress management, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining healthy cholesterol levels.
The Role of Exercise
Regular exercise is a crucial component of managing cholesterol levels. Physical activity helps raise high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, the “good” cholesterol, while lowering low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, the “bad” cholesterol. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week.
Some effective types of exercise for improving cholesterol levels include:
- Brisk walking
- Swimming
- Cycling
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT)
Incorporating strength training exercises into your routine can also be beneficial, as it helps build muscle mass, which further supports overall metabolic health.
| Type of Exercise | Benefits for Cholesterol |
|---|---|
| Brisk Walking | Improves cardiovascular health, raises HDL |
| Swimming | Low-impact, improves cardiovascular health, lowers LDL |
| Cycling | Enhances cardiovascular fitness, raises HDL |
Stress Management Techniques
Chronic stress can negatively impact cholesterol levels by increasing the production of cortisol, a hormone that can raise LDL cholesterol. Effective stress management techniques are essential for maintaining healthy cholesterol levels.
Some stress management techniques include:
- Meditation and mindfulness practices
- Yoga
- Deep breathing exercises
- Progressive muscle relaxation
By incorporating these lifestyle changes into daily life, individuals can better manage their cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. Regular physical activity and effective stress management are key components of a comprehensive approach to maintaining healthy cholesterol levels.
Medical Treatments and Cholesterol Management
Understanding the available medical treatments is essential for effective cholesterol management. High cholesterol can have significant implications on heart health, making it crucial to monitor cholesterol levels regularly. Medical treatments offer a range of options for managing cholesterol, from conventional medications to alternative therapies.
Statins and Other Medications
Statins are among the most commonly prescribed medications for lowering cholesterol. They work by inhibiting the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which plays a key role in cholesterol production in the liver. Examples of statins include atorvastatin and simvastatin. Other medications, such as bile acid sequestrants and cholesterol absorption inhibitors, may also be used to manage cholesterol levels.
“Statins have been shown to significantly reduce the risk of major vascular events in patients at high risk,” as noted in various clinical guidelines. These medications are often recommended for individuals with high cholesterol or those at increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
Alternative Therapies and Supplements
In addition to conventional medications, some individuals may consider alternative therapies and supplements to help manage their cholesterol levels. Plant sterols and stanols, for example, have been shown to help lower LDL cholesterol when consumed as part of a diet low in saturated fat and cholesterol.
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Berberine
- Soluble fiber supplements
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before adding any supplements to your regimen, as they can interact with other medications or have side effects.
Managing cholesterol effectively often requires a combination of lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and medical treatments. By understanding the available options and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals can develop a personalized plan to manage their cholesterol levels and reduce their risk of heart disease.
The Future of Cholesterol Research
As medical research continues to evolve, the management of cholesterol levels is becoming increasingly sophisticated. Ongoing studies are focused on developing more accurate and convenient methods for monitoring cholesterol levels, which is crucial for maintaining healthy cholesterol levels.
Advancements in Testing Technology
Innovations in cholesterol testing are making it easier for individuals to monitor their cholesterol levels regularly. New technologies, such as portable testing devices and advanced laboratory analysis, are improving the accuracy and accessibility of cholesterol testing.
Emerging Trends in Treatment
Research into new treatments and prevention strategies is also underway. Emerging trends include the development of novel medications and alternative therapies aimed at improving healthy cholesterol levels and reducing the risk of heart disease. By staying informed about these advancements, individuals can work with their healthcare providers to develop effective plans for managing their cholesterol levels.
FAQ
What is considered a healthy cholesterol level?
How often should I check my cholesterol levels?
Can diet alone manage cholesterol levels?
What are the risks of having low cholesterol?
How does physical activity impact cholesterol levels?
Are there any medications that can help manage cholesterol?
What is the ideal ratio of HDL to LDL cholesterol?
Can stress affect my cholesterol levels?
How do genetics influence cholesterol levels?
What are the guidelines for cholesterol levels in children?
This post contains affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases